Company News
Some basic knowledge about optical fibres.
⭕ What is optical fibre communications?
➡️ is a communication mode in which light waves are used as information carriers and optical fibres are used as transmission media.
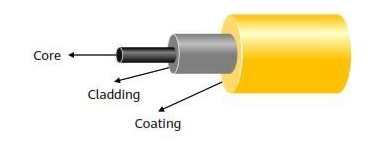
⭕ Optical Fibre Structure:
➡️ Optical fibres are made of glass. The main component is silicon dioxide(Sio2).
➡️ An optical fibre consists of a fibre core, cladding and coating.
➡️ The fibre core and cladding are made of glass (silicon dioxide) materials with different refractive indices. The outer layer is a flexible and wearable plastic sheath.
➡️ The fibre core is used to transmit optical signals, the cladding is used to protect the fibre core and control signal transmission, and the coating is the outermost layer of the optical fibre, including the primary coating layer, buffer layer, and secondary coating layer.
➡️ The coating protects the optical fibre from water corrosion and mechanical damage and improves the mechanical strength and flexibility of the optical fibre, thus prolonging the service life of the optical fibre.
⭕ Basic principle of optical signal transmission
➡️ Optical communication utilises the principle of total internal reflection.
➡️The necessary conditions for optical signal transmission in an optical fibre are:
1️⃣ Fibre core refractive index is greater than the Cladding refractive index
2️⃣ The incident angle is greater than the critical angle.
⭕ Classification of optical fibres
➡️ The number of transmission modes in an optical fibre varies according to the diameter of the fibre core.
➡️ Optical fibres can be classified into single-mode and multi-mode optical fibres by the number of transmission modes.
1️⃣ Multi-Mode:
? The diameter of a fibre core is much greater than that of the optical wavelength, and optical signals are transmitted in dozens or more modes in the fibre.
? The core diameter is 50 µm to 62.5 µm.
? Generally, multi-mode fibres are orange and marked MM.
? Multi-mode fibres are usually printed with MM, OM3, 50/125, or 62.5/125.
? They feature short transmission distances, easy processing, and low cost.
? suitable for short-distance transmission and low-speed data communication.
2️⃣ Single Mode:
? The fibre core is small and is of the same order of magnitude as the optical wavelength; the fibre allows only one transmission mode.
? The core diameter is 5–10 µm
? Single-mode fibres are yellow and marked SM.
? Single-mode fibres are usually printed with SM, G652, G655, G657, or 9/125
? They feature high speed, low loss, and high bandwidth
? suitable for long-distance transmission and high-speed communication.